The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is an air conditioning efficiency rating. Your unit's SEER rating is the difference between two measurements: BTUs divided by watts per hour (Wh). So, SEER = BTU / Wh, and the higher the SEER, the more efficiency you are receiving from your air conditioning unit.
Why is the SEER rating important to me, you ask? The answer: both savings and a reduction in your carbon footprint! The typical reduction of your energy cost upgrading from a 10 SEER unit to a 15 SEER unit is 37% annually! In this example alone, your household could pocket hundreds of dollars each year, while positively affecting our environment! The Department of Energy (DOE) implemented new minimum efficiency standards for residential and commercial HVAC equipment; however, standards differ by region.
Have a heating, cooling, or plumbing problem, but no time to wait for a repairman? Need a second opinion on an existing quote?
We’ll give you free advice about your question or problem. In many cases, you’ll get an estimate or the help you need during the video call.
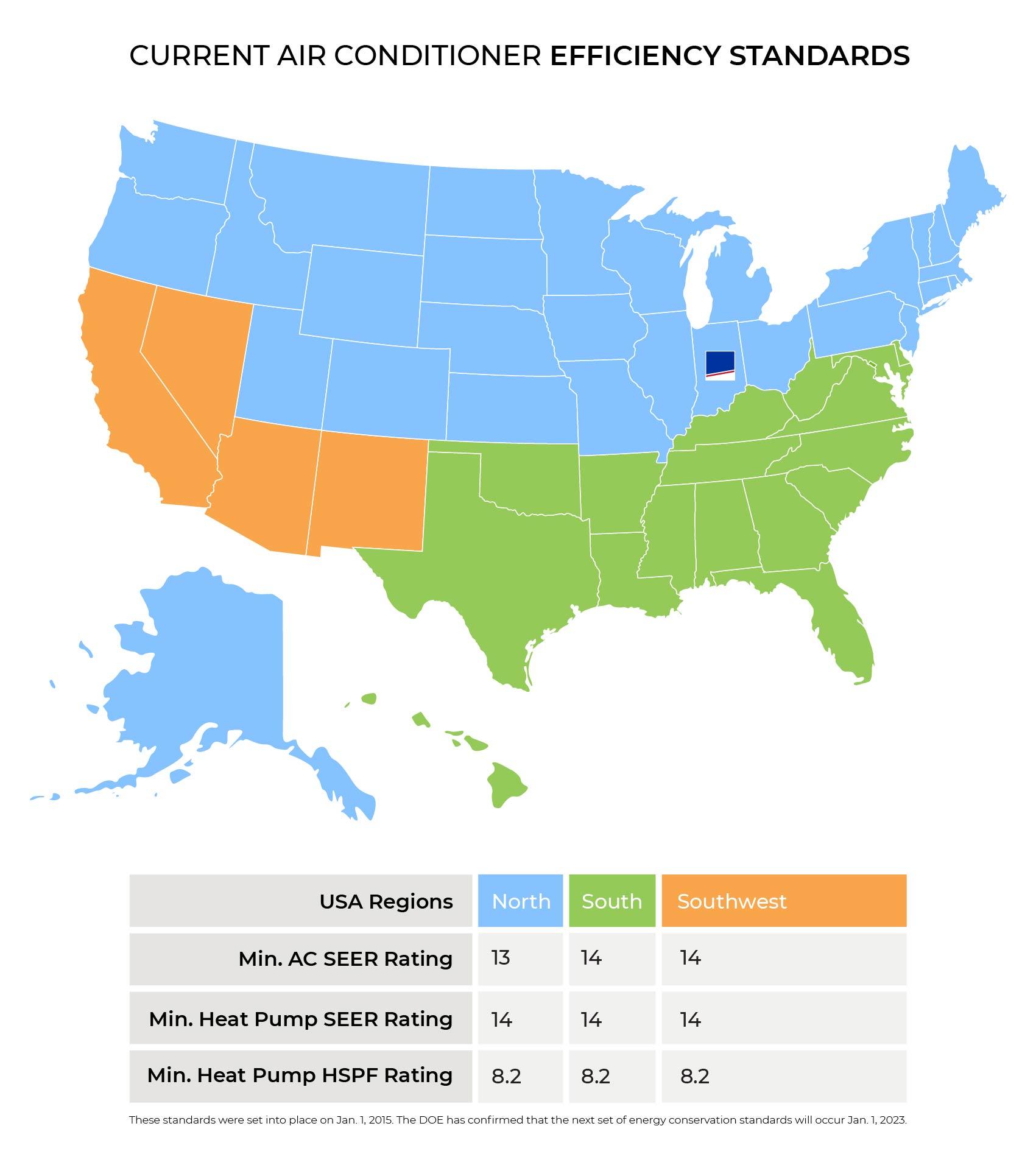
The rationale for regional standards is that the United States climate varies enormously and evaluating the cost-effectiveness more appropriately for different locations will ensure cost-effective efficiency. The former 13 SEER air conditioning standards have changed to 14 SEER in most of the country, with 13 SEER still acceptable in northern states. In all regions, split-system heat pumps will move an increase in efficiency from 13 SEER and 7.7 HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) to the new minimum of 14 SEER and 8.2 HSPF.
What are the air conditioner standards for efficiency in 2020?
The United States is divided into three separate regions, each with different efficiency standards. The map below shows the current minimum SEER and HSPF ratings by state:
How to find your SEER rating
Find the BTUs/hour and the watts used/hour of your air conditioner (found on the machine itself, in its operating manual, or through the manufacturer’s website), and divide the BTUs by the watt-hours.
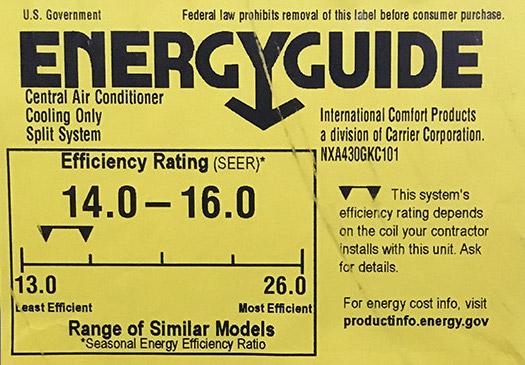 Many newer air conditioning units have a large, yellow EnergyGuide sticker that will clearly identify your unit's SEER rating. If you find that your unit doesn't have this yellow sticker, you may be able to find this information on your air handler.
Many newer air conditioning units have a large, yellow EnergyGuide sticker that will clearly identify your unit's SEER rating. If you find that your unit doesn't have this yellow sticker, you may be able to find this information on your air handler.
If you're unable to find your SEER information by these two methods, you can also try contacting your unit's manufacturer. Be sure to have your model number and serial number on hand when you contact them.
AC Tonnage
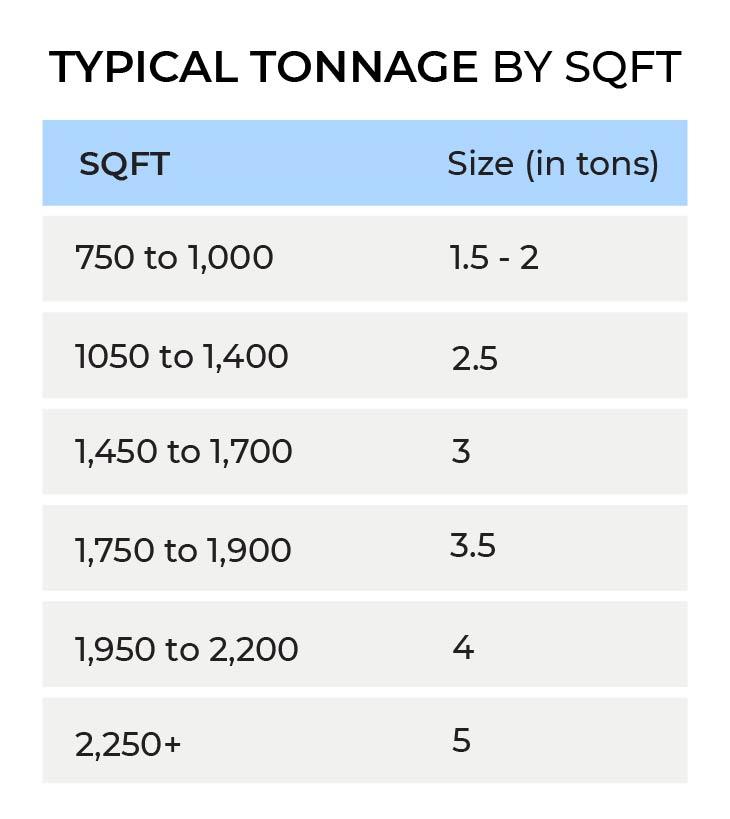
While the term "tonnage" may imply the physical weight or "size" of an air conditioner, it actually refers to the unit's cooling capabilities. AC tonnage specifically measures how much heat the unit is able to remove in an hour's time. For example, a one-ton AC unit can effectively remove 12,000 BTUs from a home in just one hour. As the number of tons doubles, so does the amount of BTUs removed.
In order to determine what "size" unit you need, you'll need to consider the square footage of your home, the number of occupants, and the amount of windows. Take a look at the chart to see what size unit will work best for your home. Depending on these factors, you may need more than one unit for your home as anything over 5 tons is considered a commercial size unit, which is unavailable for residential homes.
If you have additional questions on how the federal minimum SEER rating may affect you, please do not hesitate to contact Commercial Service. Schedule an appointment with our easy Online Scheduling or by calling 812-339-9114



